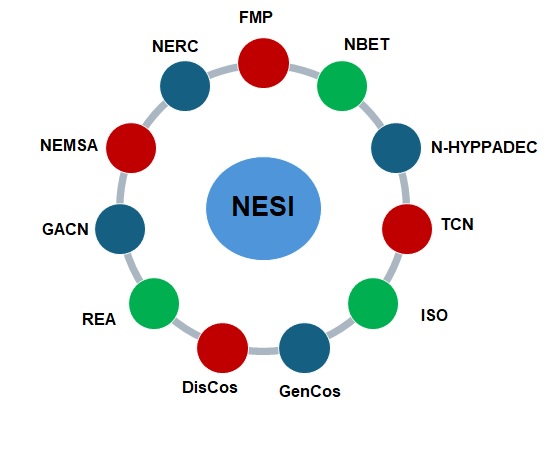
Independent Power Producers (IPPs)
IPP is an abbreviation for Independent Power Producer. This refers to company, state or organisation that produces electricity apart from the Federal Government.
Activities of IPPs are guided by law separately written in a document called Power Production Agreement (PPA) for a specific IPP. General rules guiding establishment of IPP activities are contained in both the repealed Electric Power Reform Act, 2005 and the
Electricity Act 2023.
Due to dire demand for more electricity in Nigeria to bridge the wide gap between total available generation and the electricity demand in the late nineties, the Federal Government of Nigeria entered into
contract with AES company in 2001. AES company was able to augment Grid electric power with 270 MW produced from barges brought to the country from oversea within short period. That was a great relief as loadshedding dropped and the power grid was more stable.
Following the enactment of Electric Power Reform Act 2005, companies and states were motivated to enter into the electricity production business. Since 2005, there have been tremendous increase in the number of IPPs in Nigeria.
Also, the Federal Government of Nigeria embarked on several power production projects called National Integrated Power Projects (NIPP). However, NIPP activities transcended electricity projects as transmission and distribution networks expansion were later included.
The table below list all the power station connected to the Nigeria transmission system - including Hydro stations owned by the Federal Government, IPPs and NIPPs.